| Codeforces Round 896 (Div. 1) |
|---|
| Finished |
During the summer vacation after Zhongkao examination, Tom and Daniel are planning to go traveling.
There are $$$n$$$ cities in their country, numbered from $$$1$$$ to $$$n$$$. And the traffic system in the country is very special. For each city $$$i$$$ ($$$1 \le i \le n$$$), there is
- a road between city $$$i$$$ and $$$2i$$$, if $$$2i\le n$$$;
- a road between city $$$i$$$ and $$$2i+1$$$, if $$$2i+1\le n$$$.
Making a travel plan, Daniel chooses some integer value between $$$1$$$ and $$$m$$$ for each city, for the $$$i$$$-th city we denote it by $$$a_i$$$.
Let $$$s_{i,j}$$$ be the maximum value of cities in the simple$$$^\dagger$$$ path between cities $$$i$$$ and $$$j$$$. The score of the travel plan is $$$\sum_{i=1}^n\sum_{j=i}^n s_{i,j}$$$.
Tom wants to know the sum of scores of all possible travel plans. Daniel asks you to help him find it. You just need to tell him the answer modulo $$$998\,244\,353$$$.
$$$^\dagger$$$ A simple path between cities $$$x$$$ and $$$y$$$ is a path between them that passes through each city at most once.
The first line of input contains a single integer $$$t$$$ ($$$1\le t\le 200$$$) — the number of test cases. The description of test cases follows.
The only line of each test case contains two integers $$$n$$$ and $$$m$$$ ($$$1\leq n\leq 10^{18}$$$, $$$1\leq m\leq 10^5$$$) — the number of the cities and the maximum value of a city.
It is guaranteed that the sum of $$$m$$$ over all test cases does not exceed $$$10^5$$$.
For each test case output one integer — the sum of scores of all possible travel plans, modulo $$$998\,244\,353$$$.
53 12 210 943 20154 147
6 19 583217643 68816635 714002110
In the first test case, there is only one possible travel plan:
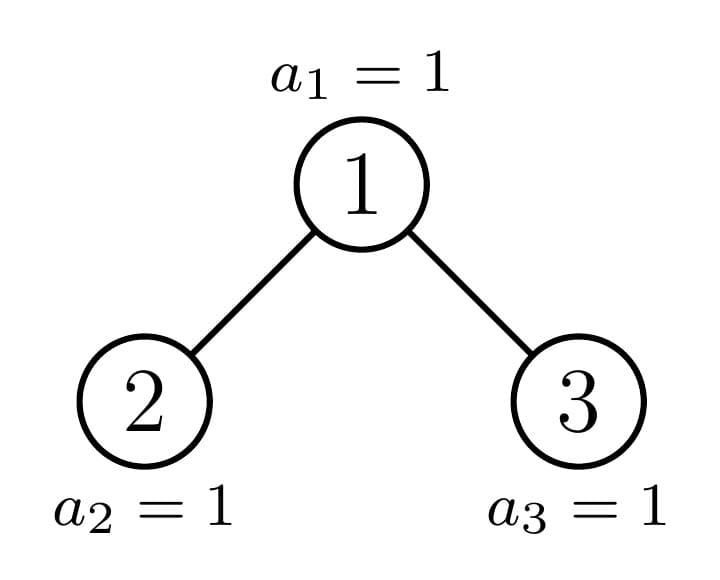
Path $$$1\rightarrow 1$$$: $$$s_{1,1}=a_1=1$$$.
Path $$$1\rightarrow 2$$$: $$$s_{1,2}=\max(1,1)=1$$$.
Path $$$1\rightarrow 3$$$: $$$s_{1,3}=\max(1,1)=1$$$.
Path $$$2\rightarrow 2$$$: $$$s_{2,2}=a_2=1$$$.
Path $$$2\rightarrow 1\rightarrow 3$$$: $$$s_{2,3}=\max(1,1,1)=1$$$.
Path $$$3\rightarrow 3$$$: $$$s_{3,3}=a_3=1$$$.
The score is $$$1+1+1+1+1+1=6$$$.
In the second test case, there are four possible travel plans:
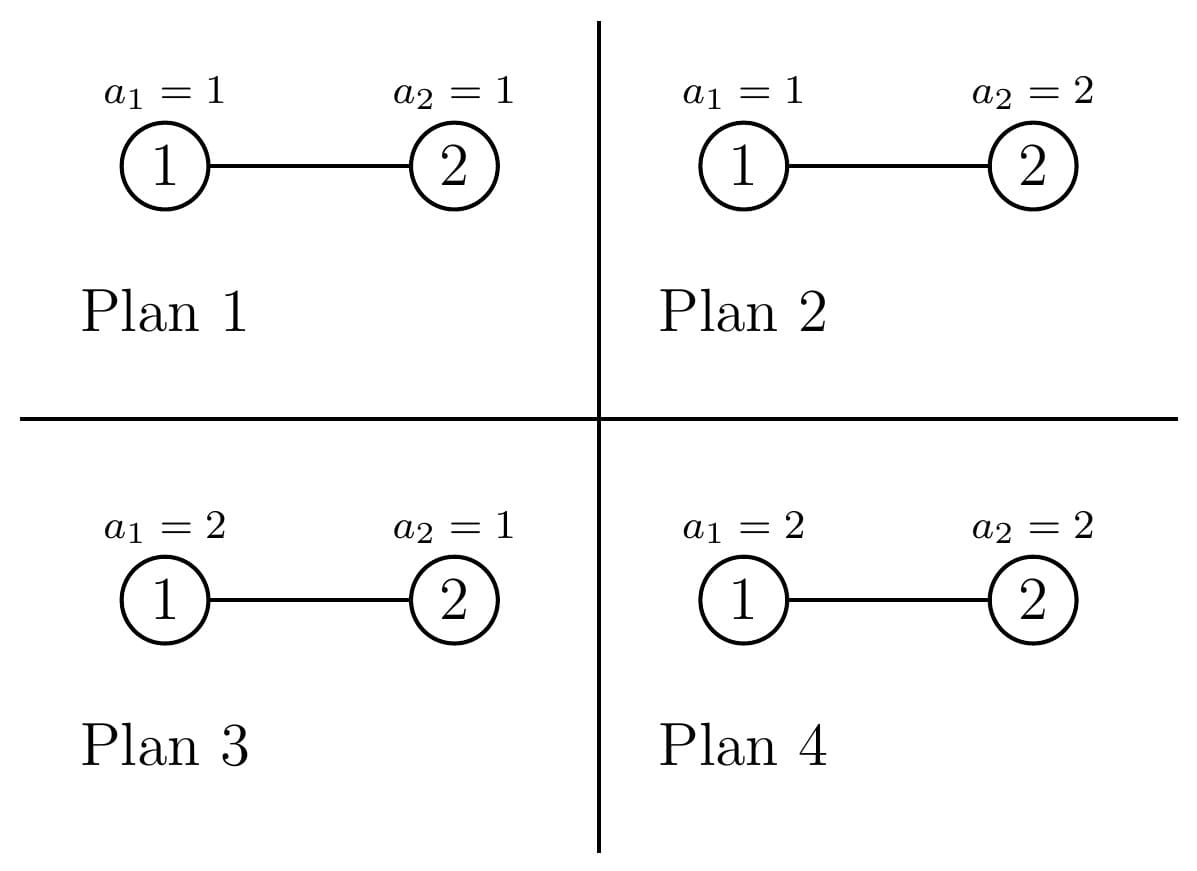
Score of plan $$$1$$$: $$$1+1+1=3$$$.
Score of plan $$$2$$$: $$$1+2+2=5$$$.
Score of plan $$$3$$$: $$$2+2+1=5$$$.
Score of plan $$$4$$$: $$$2+2+2=6$$$.
Therefore, the sum of score is $$$3+5+5+6=19$$$.
| Name |
|---|




