| Codeforces Round 937 (Div. 4) |
|---|
| Finished |
Find the minimum height of a rooted tree$$$^{\dagger}$$$ with $$$a+b+c$$$ vertices that satisfies the following conditions:
- $$$a$$$ vertices have exactly $$$2$$$ children,
- $$$b$$$ vertices have exactly $$$1$$$ child, and
- $$$c$$$ vertices have exactly $$$0$$$ children.
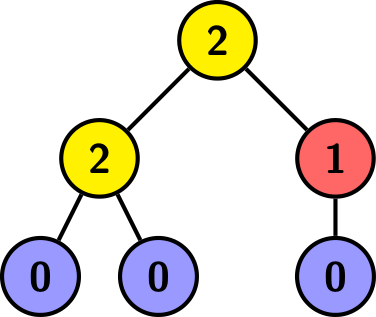
The tree above is rooted at the top vertex, and each vertex is labeled with the number of children it has. Here $$$a=2$$$, $$$b=1$$$, $$$c=3$$$, and the height is $$$2$$$.
$$$^{\dagger}$$$ A rooted tree is a connected graph without cycles, with a special vertex called the root. In a rooted tree, among any two vertices connected by an edge, one vertex is a parent (the one closer to the root), and the other one is a child.
The distance between two vertices in a tree is the number of edges in the shortest path between them. The height of a rooted tree is the maximum distance from a vertex to the root.
The first line contains an integer $$$t$$$ ($$$1 \leq t \leq 10^4$$$) — the number of test cases.
The only line of each test case contains three integers $$$a$$$, $$$b$$$, and $$$c$$$ ($$$0 \leq a, b, c \leq 10^5$$$; $$$1 \leq a + b + c$$$).
The sum of $$$a + b + c$$$ over all test cases does not exceed $$$3 \cdot 10^5$$$.
For each test case, if no such tree exists, output $$$-1$$$. Otherwise, output one integer — the minimum height of a tree satisfying the conditions in the statement.
102 1 30 0 10 1 11 0 21 1 33 1 48 17 924 36 481 0 00 3 1
2 0 1 1 -1 3 6 -1 -1 3
The first test case is pictured in the statement. It can be proven that you can't get a height smaller than $$$2$$$.
In the second test case, you can form a tree with a single vertex and no edges. It has height $$$0$$$, which is clearly optimal.
In the third test case, you can form a tree with two vertices joined by a single edge. It has height $$$1$$$, which is clearly optimal.
| Name |
|---|




